DB
[DB] JDBC란?
하부루
2024. 7. 20. 20:09
스프링 DB 1편 - 데이터 접근 핵심 원리 강의 | 김영한 - 인프런
김영한 | 백엔드 개발에 필요한 DB 데이터 접근 기술을 기초부터 이해하고, 완성할 수 있습니다. 스프링 DB 접근 기술의 원리와 구조를 이해하고, 더 깊이있는 백엔드 개발자로 성장할 수 있습니
www.inflearn.com
1. JDBC 등장 이유
- 애플리케이션을 개발 할 때 데이터는 대부분 데이터베이스에 보관한다.
- 클라이언트가 애플리케이션 서버를 통해 데이터를 저장하거나 조회하면, 애플리케이션 서버는 다음 과정을 통해서 데이터베이스를 사용한다.
[애플리케이션 서버와 DB - 일반적인 사용법]
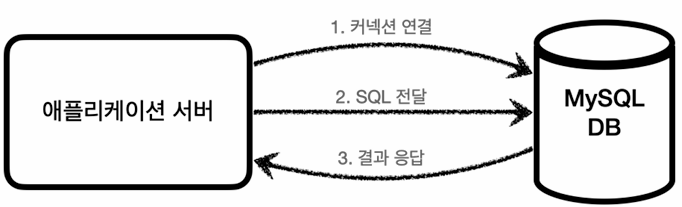
- 커넥션 연결: 주로 TCP/IP를 사용해서 커넥션을 연결.
- SQL 전달: 애플리케이션 서버는 DB가 이해할 수 있는 SQL을 연결된 커넥션을 통해 DB에 전달.
- 결과 응답: DB는 전달된 SQL을 수행하고 결과를 반환. 애플리케이션 서버는 응답를 결과 활용.
[만약에 DB가 변경이 된다면 생길 수 있는 문제점]
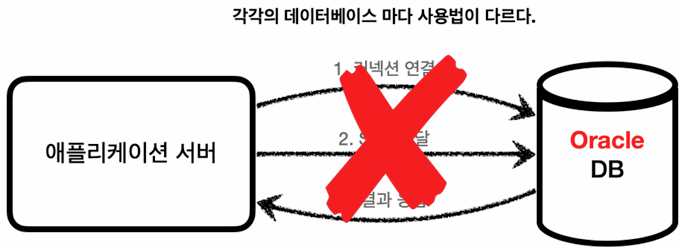
- 문제는 각각의 DB마다 커넥션을 연결하는 방법, SQL을 전달하는 방법, 결과를 받는 방법이 모두 다르다는 것이다.
- DB를 다른 종류의 DB로 변경하면 애플리케이션 서버에 개발된 DB 사용 코드도 변경해야 한다.
- 개발자가 각각의 데이터베이스마다 커넥션 연결, SQL 전달, 그리고 그 결과를 응답 받는 방법을 새로 학습해야 한다.
이러한 문제를 해결하기 위해 JDBC라는 자바 표준이 등장.
2. JDBC 표준 인터페이스
[JDBC는 대표적으로 다음 3가지 기능을 표준 인터페이스로 정의하여 제공]
- java.sql.Connection: 연결
- java.sql.Statement: SQL을 담은 내용
- java.sql.ResultSet: SQL 요청 응답

[MySQL & Oracle 드라이버 사용]


[JDBC의 등장으로 해결된 문제]
- 애플리케이션 로직은 이제 JDBC 표준 인터페이스에만 의존한다. 따라서 DB를 다른종류의 DB로 변경하고 싶으면 JDBC 구현 라이브러리만 변경하면 된다.
- 개발자는 JDBC 표준 인터페이스 사용법만 알면 된다.
[JDBC 표준화의 한계]
- JDBC의 등장으로 많은 것이 편리해졌지만, 각각의 데이터베이스마다 SQL, 데이터타입 등의 일부 사용법 다르다.
- 결국 데이터베이스를 변경하면 JDBC 코드는 변경하지 않아도 되지만 SQL은 해당 데이터베이스에 맞도록 변경해야한다.
- 참고로 JPA(Java Persistence API)를 사용하면 이렇게 각각의 데이터베이스마다 다른 SQL을 정의해야 하는 문제도 많은 부분 해결할 수 있다.
3. JDBC 최신 데이터 접근 기술
- JDBC는 오래된 기술이고, 사용하는 방법도 복잡하다. 그래서 최근에는 JDBC를 직접 사용하기 보다는 JDBC를 편리하게 사용하는 다양한 기술이 존재한다.
- 대표적으로 SQL Mapper와 ORM 기술로 나눌 수 있다.

[SQL Mapper]
- 장점
- JDBC를 편리하게 사용하도록 도와준다.
- SQL 응답 결과를 객체로 편리하게 변환해준다.
- JDBC의 반복 코드를 제거해준다.
- 단점
- 개발자가 SQL을 직접 작성해야한다.
[ORM 기술]
- ORM은 객체를 관계형 데이터베이스 테이블과 매핑해주는 기술이다.
- 이 기술 덕분에 개발자는 반복적인SQL을 직접 작성하지 않고, ORM 기술이 개발자 대신에 SQL을 동적으로 만들어 실행해준다.
- 추가로 각각의 데이터베이스마다 다른 SQL을 사용하는 문제도 중간에서 해결해준다.
- 대표 기술: JPA, 하이버네이트, 이클립스링크

[SQL Mapper vs ORM 기술]
- SQL Mapper와 ORM 기술 둘다 각각 장단점이 있다.
- SQL Mapper는 SQL만 직접 작성하면 나머지 번거로운 일은 SQL Mapper가 대신 해결해준다.
- SQL Mapper는 SQL만 작성할 줄 알면 금방 배워서 사용할 수 있다.
- ORM기술은 SQL 자체를 작성하지 않아도 되어서 개발 생산성이 매우 높아진다. 편리한 반면에 쉬운 기술은 아니므로 실무에서 사용하려면 깊이있게 학습해야 한다.
4. DB JDBC 커넥션
[ConnectionConst.class]

[DBConnectionUtil.class]

[DriverManager]
- JDBC 인터페이스에서 구현체를 얻기위한 메소드이고, 이 커넥션은 각각 DB의 구현체를 의미.
- DriverManager가 현재 다운로드 되어있는 라이브러리 중 DB 라이브러리를 참조.
- DriverManager.getConnection() 메소드를 통해 해당 드라이버가 제공하는 커넥션을 반환.

[DriverManger.getConnection() 과정]
- 애플리케이션 로직에서 커넥션이 필요하면 DriverManager.getConnection() 을 호출.
- DriverManger는 라이브러리에 등록된 드라이버 목록을 자동으로 인식한다.
- URL: 예) jdbc:h2:tcp//localhost/~/test
- 이름, 비밀번호 등 접속에 필요한 추가 정보
- 여기서 각각의 드라이버는 URL 정보를 체크해서 본인이 처리할 수 있는 요청인지 확인.
- 예를 들어서 URL이 jdbc:h2로 시작하면 이것은 h2 데이터베이스에 접근하기 위한 규칙이다.
- 따라서 H2 드라이버는 본인이 처리할 수 있으므로 실제 데이터베이스에 연결해서 커넥션을 획득하고 이 커넥션을 클라이언트에 반환한다.
- 반면에 URL이 jdbc:h2로 시작했는데 MySQL 드라이버가 먼저 실행되면 이 경우 본인이 처리할 수 없다는 결과를 반환하게 되고, 다음 드라이버에게 순서가 넘어간다.
- 이렇게 찾은 커넥션 구현체가 클라이언트에 반환된다.
5. JDBC를 사용한 단순한 CRUD
[Member.class]
/*
* 예제를 위한 Member class
**/
@Data
public class Member {
private String memberId;
private int money;
public Member() {
}
public Member(String memberId, int money) {
this.memberId = memberId;
this.money = money;
}
}[MemberRepositoryV0.class]
/*
JDBC - DriverManager 사용
<커넥션을 얻어서 쿼리를 날리는 Repository>
!!과정 요약!!
1. getConnection 요청을 통해 커넥션을 얻는다.
2. 커넥션을 닫을 객체를 null로 초기화 하는 이유는, SQLException은 Checked Exception 이기 떄문에, try-catch로 처리
3. PreparedStatement 객체를 이용해 쿼리를 DB에 날린다.
4. 모든 처리가 완료 되었을땐, 연결된 커넥션을 순차적으로 끊어줘야한다.
5. ResultSet은 DB에서 불러온 결과를 저장해서 값을 조회하는 역할을 한다. (데이터 저장소)
*/
@Slf4j
public class MemberRepositoryV0 {
//저장
public Member save(Member member) throws SQLException {
String sql = "insert into member(member_id, money) values (?, ?)";
Connection con = null;
PreparedStatement pstmt = null;
try {
con = getConnection();
pstmt = con.prepareStatement(sql);
pstmt.setString(1, member.getMemberId());
pstmt.setInt(2,member.getMoney());
pstmt.executeUpdate();
return member;
} catch (SQLException e) {
log.error("db error", e);
throw e;
} finally {
close(con, pstmt, null);
}
}
//조회
public Member findById(String memberId) throws SQLException {
String sql = "select * from member where member_id = ?";
Connection con = null;
PreparedStatement pstmt = null;
ResultSet rs = null;
try {
con = getConnection();
pstmt = con.prepareStatement(sql);
pstmt.setString(1, memberId);
rs = pstmt.executeQuery();
if (rs.next()) {
Member member = new Member();
member.setMemberId(rs.getString("member_id"));
member.setMoney(rs.getInt("money"));
return member;
}else{
throw new NoSuchElementException("member not found memberId=" + memberId);
}
} catch(SQLException e) {
log.error("db error", e);
throw e;
} finally {
close(con, pstmt, rs);
}
}
//수정
public void update(String memberId, int money) throws SQLException {
String sql = "update member set money=? where member_id=?";
Connection con = null;
PreparedStatement pstmt = null;
try {
con = getConnection();
pstmt = con.prepareStatement(sql);
pstmt.setInt(1, money);
pstmt.setString(2,memberId);
int resultSize = pstmt.executeUpdate();
log.info("resultSize={}", resultSize);
} catch (SQLException e) {
log.error("db error", e);
throw e;
} finally {
close(con, pstmt, null);
}
}
//삭제
public void delete(String memberId) throws SQLException {
String sql = "delete from member where member_id=?";
Connection con = null;
PreparedStatement pstmt = null;
try {
con = getConnection();
pstmt = con.prepareStatement(sql);
pstmt.setString(1,memberId);
pstmt.executeUpdate();
} catch (SQLException e) {
log.error("db error", e);
throw e;
} finally {
close(con, pstmt, null);
}
}
//커넥션 닫기
private void close(Connection con, Statement stmt, ResultSet rs) {
if (rs != null) {
try {
rs.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
log.info("error", e);
}
}
if (stmt != null) {
try {
stmt.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
log.info("error", e);
}
}
if (con != null) {
try {
con.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
log.info("error", e);
}
}
}
//커넥션 얻기
private Connection getConnection() {
return DBConnectionUtil.getConnection();
}
}[MemberRepositoryV0Test.class]
@Slf4j
class MemberRepositoryV0Test {
MemberRepositoryV0 repository = new MemberRepositoryV0();
@Test
void crud() throws SQLException {
//save
Member member = new Member("member7", 10000);
repository.save(member);
//findById
Member findMember = repository.findById(member.getMemberId());
assertThat(findMember).isEqualTo(member);
//update: moneoy : 10000 -> 20000
repository.update(member.getMemberId(), 20000);
Member updatedMember = repository.findById(member.getMemberId());
assertThat(updatedMember.getMoney()).isEqualTo(20000);
//delete
repository.delete(member.getMemberId());
assertThatThrownBy(() -> repository.findById(member.getMemberId()))
.isInstanceOf(NoSuchElementException.class);
}
}